
CMB คืออะไร ?
รังสีไมโครเวฟพื้นหลังของเอกภพ หรือ CMB เป็นแสงที่เก่าแก่ที่สุดที่เราสามารถมองเห็นได้ในปัจจุบัน CMB ได้กำเนิดขึ้นเมื่อครั้งจักรวาลมีอายุราว 380,000 ปี ในช่วงเวลานั้น จักรวาลได้ขยายตัวจนมีขนานใหญ่เพียงพอ จนกระทั้งโฟตอนมาสามารถเดินทางได้อย่างอิสระ โดยไม่ถูกกักกันโดยอนุภาคอิสระที่อยู่ในช่วงเวลาดังกล่าว จากช่วงเวลานั้นจนถึงปัจจุบัน จักรวาลได้ทำการขยายตัว และเย็นตัวลงเป็นระยะเวลามากกว่า 13 หมื่นล้านปี ความยาวคลื่นของ CMB ก็ได้ขยายตัวขึ้น ตามการขยายตัวของจักรวาล (redshift) นอกจากนั้น อุณหภูมิของ CMB โฟตอนก็ได้ลดลงจนเหลือประมาณ 2.7 K.
เนื่องจาก CMB เป็นแสงที่เราสามารถศึกษาได้ไกลที่สุดเท่าที่เป็นไปได้ มันจึงเป็นหลักฐานสำคัญที่สามารถช่วยให้เราเข้าใจจุดกำเนิดของจักรวาล นอกจากนั้นเพราะกว่าที่ CMB จะเดินทางมาถึงโลกมนุษย์ในปัจจุบัน มันต้องเดินทางผ่าน สิ่งต่าง ๆ มากมายในจักรวาลทั้ง กาแล็คซี่ หรือ โครงสร้างขนาดใหญของเอกภพ (large-scale structure) ทุกครั้งที่ CMB โฟตอนเดินทางผ่าน แรงโน้มถ่วงจะทำให้คุณสมบัติบางอย่างของ CMB เปลี่ยนไป และการเปลี่ยนแปลงของ CMB นี้เองที่ทำให้เราสามารถเข้าใจในโครงสร้างและองค์ประกอบของจักรวาล
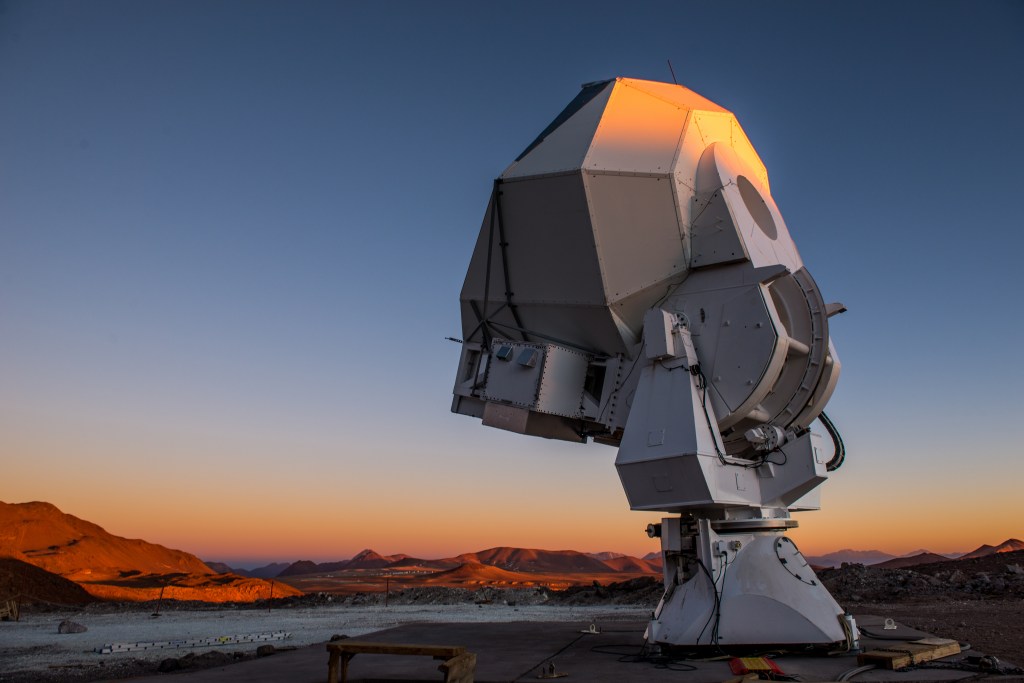

The Huan Trans Telescope holding the POLARBEAR receiver at the James Ax Observatory, Chile
ทำความรู้จัก POLARBEAR
POLARBEAR is a CMB polarization measurement located in the northern Chile. Our primary goal is to detect a faint CMB B-mode which is the evidence of the inflationary theories. The inflationary theories predicted that the early universe went through a phase of rapidly expansion which generated the primordial gravitational wave. These gravitational wave also imprinted its signature, a primordial B-mode polarization, into the CMB polarization.
Additionally, the gravity from the early time influence the universe to form large-scale structures which can be observed in the present time. These structures distorted the early CMB photon and transform E-mode polarization to B-mode polarization. The measurements from POLARBEAR could also help us understand more the components of the universe include the neutrino mass and dark energy.
POLARBEAR was deployed in the Atacama desert in October 2011 and got a first in January 2012. Since then the POLARBEAR collaboration has been publishing numerous publications include the first detection of the B-mode polarization produced by the gravitational lensing in 2014 (more detail).
อะไรคือ Simons Array
The Simons Array is the expansion of the POLARBEAR experiment. When it is completed, it will consist of three telescopes. Each of these will be deployed with more than 7,500 dual-polarization detectors. Combines three receivers, the Simons Arrays will have more than 22,000 detectors which are 18 times more than the POLARBEAR. Those increased in the number of detectors and more advanced readout technology, help us enhance the capacity of the detection of the B-mode polarization from the inflation (more detail) .

Why Chile?
It is well-known that the atmospheric water vapor is the obstructed of millimeter-wave astronomy due to the absorption and the attenuation in the millimeter-wave. With an elevation of more than 5000 meters above sea level, the Atacama desert in Chile has been recognized as one of the dryest places in the world. This is why many astronomical sites are located in this area include POLARBEAR.

Want to know more?
Here is a selected list of paper about the POLARBEAR and the Simons Array.
- Z. Kermisha, P. Ade, A. Anthony et.,al. “The POLARBEAR experiment,” Proc. SPIE 8452, Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VI, 84521C (24 September 2012); doi: 10.1117/12.926354
- N. Stebor, P. Ade, Y. Akiba, et.,al. “The Simons Array CMB polarization experiment,” Proc. SPIE 9914, Millimeter, Submillimeter, and Far-Infrared Detectors and Instrumentation for Astronomy VIII, 99141H (20 July 2016); https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2233103
- The POLARBEAR Collaboration. “A MEASUREMENT OF THE COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND B-MODE POLARIZATION POWER SPECTRUM AT SUB-DEGREE SCALES WITH POLARBEAR,” ApJ, 794, 171, 2014. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/794/2/171
“The Universe is under no obligation to make sense to you.”
Neil deGrasse Tyson